Toyota Tundra Problems: Top Complaints & Fixes
The Toyota Tundra is known for its strength and reliability. It’s a full-size pickup truck with powerful V8 engines and great off-road skills. Many people use their Tundras for work and fun.
But, some model years have big reliability problems. These common Tundra issues include frame rust, transmission failures, and expensive engine fixes. Not all years are as reliable as others.
Knowing which years to avoid can save you a lot of money. This guide covers the most common Toyota truck problems and how to fix them. It’s for current owners and those thinking of buying a Tundra.
Our experts have found the problem years and solutions. You’ll learn how to spot issues, what repairs cost, and how to prevent big problems.
Key Takeaways
- Certain Tundra model years have significant reliability problems despite the brand’s reputation
- Frame rusting, transmission issues, and engine failures are the most common complaints
- Knowing problematic years can help buyers avoid costly repairs
- Early detection and proper maintenance can prevent many major issues
- Professional diagnosis is essential for complex transmission and engine problems
- Some problems have recalls or extended warranties available from Toyota
Understanding Your Toyota Tundra’s Most Common Issues
Spotting Toyota Tundra common problems early can save you a lot of money. It also helps avoid being stuck on the side of the road. Even though the Tundra is known for being tough, some issues pop up more often than others.
Frame rust and corrosion are big worries for 2000-2006 Tundras. Toyota had to recall these models and offer extended warranties because of it. The rust usually starts where salt and water collect.
For 2007-2012 Tundras, air injection pump failure is a big problem. This part, which helps with emissions, often breaks down early. It can turn on the check engine light and lead to expensive fixes if not fixed right away.
CarComplaints.com says engine troubles are the worst category for Tundra issues. These can include too much oil use or timing chain failures. Fixing these can cost over $3,000.
Other common problems include transmission failures, brake booster issues, and electrical problems. Transmission troubles can cause rough shifting or complete failure. Brake booster issues can make braking less effective.
The 2012 model year is known for being extra problematic. It had higher repair costs and issues happened sooner than in other years. This makes it a year to be careful about in the used truck market.
Electrical problems can affect many systems, like dashboard lights and power accessories. These issues can be hard to diagnose without the right Toyota truck troubleshooting methods.
Knowing about these common issues helps you catch problems early. Regular maintenance and quick action to unusual signs can stop small issues from becoming big ones. Most importantly, it lets you make smart choices about repairs and upkeep.
Transmission Problems and Step-by-Step Solutions
Your Toyota Tundra’s transmission is key, and spotting early signs can save you a lot. Toyota Tundra transmission problems hit 2007-2009 models hard, with repair costs from $3,000 to $4,500. The 6-speed automatic in these years often fails early, before 100,000 miles.
Issues like hard shifting, slipping, and total failure don’t happen fast. They creep up, giving you time to act if you know what to look for.
Recognizing Warning Signs Early
Transmission failure symptoms start small before becoming big problems. Notice if shifting from park to drive is slow. This means wear inside that will get worse.
Listen for odd sounds when shifting gears. Grinding, whining, or clunking means something’s wrong inside. Tundra shifting issues also include rough or jerky shifts, mainly when speeding up.
Regularly check your transmission fluid. If it’s dark or smells burnt, it’s overheated and damaged. Low fluid makes shifting poor and wears out parts faster.
Diagnostic Steps for Transmission Issues
Begin by checking the transmission fluid level and color. Use the dipstick with the engine running and transmission warm. Clean, red fluid is good; dark or burnt means trouble.
Drive your Tundra through all gears, noting any odd behavior. Notice how it shifts cold versus warm. Keep a record of any odd shifts to help mechanics find the problem.
Use an OBD-II scanner to find error codes related to the transmission. These codes tell you which parts are failing and help pinpoint the issue.
Choosing Between Professional and DIY Repairs
DIY fans can handle simple tasks like fluid changes and filter swaps. But, fixing the transmission itself needs special tools and skills most don’t have.
Think about transmission repair costs when deciding. Professional checks cost $100-200 but can save you from big mistakes. Big repairs or rebuilds should be done by pros to ensure they’re done right and covered by warranty.
If your Tundra has many symptoms or is old, get a pro to check it. Trying big repairs yourself can cause more damage and cost more in the end.
Air Injection Pump Failure: Diagnosis and Repair Guide
Knowing the signs of air injection pump failure can save you a lot of money on your Toyota Tundra. This system adds fresh air to the exhaust to cut down on pollutants. If it breaks, it’s one of the priciest problems for your Tundra.
The 2007-2012 Tundra models are hit the hardest by air injection system failures. Replacing both the pump and control module can cost between $1,800 and $3,000. Unfortunately, Toyota’s warranty usually doesn’t cover these repairs.
How to Recognize Air Injection Pump Symptoms
There are several signs that your Tundra’s air injection pump might be failing. A constant check engine light that won’t go away after simple checks is a common sign. Your truck might also go into limp mode, limiting how fast it can go.
You might hear strange noises like rattling or grinding when you start the engine. These sounds happen when the pump can’t work right. Cold weather makes these problems more obvious.
Testing Your Air Injection System
To check your air injection system, you need an OBD-II scanner to look at diagnostic codes. Codes like P0410, P0411, and P0418 usually mean there’s a problem with the system.
Looking at the system visually can show you cracked vacuum lines or loose connections. Listen for the pump’s sound during cold starts. No sound usually means the pump has failed.
Step-by-Step Air Injection Pump Replacement
Fixing the air injection system involves removing the engine cover and disconnecting the battery. The pump is near the firewall on the passenger side. You’ll need basic tools and about four hours to do it.
It’s best to replace both the pump and control module at the same time to avoid future problems. Aftermarket parts are 30-40% cheaper than OEM ones but reliable. Getting a pro to do the job ensures everything works right and you might get warranty coverage.
| Component | OEM Cost | Aftermarket Cost | Labor Hours |
|---|---|---|---|
| Air Injection Pump | $1,200-$1,500 | $800-$1,000 | 3-4 hours |
| Control Module | $400-$600 | $250-$400 | 1-2 hours |
| Complete System | $1,800-$2,400 | $1,200-$1,800 | 4-5 hours |
| Professional Labor | $400-$600 | $400-$600 | Variable |
Engine Performance Issues: Complete Troubleshooting Guide
Your Toyota Tundra’s engine is its heart. But, it can face serious problems that need quick action. Toyota Tundra engine problems are among the most severe, according to car complaint sites. The 2008 model year had major camshaft failures in the 5.7L V8 engine, costing $2,000 to $4,000 to fix.
Engine troubles don’t always show up suddenly. They might start with small changes in how your truck runs. Catching these signs early can prevent engine failure.
Identifying Common Engine Warning Signs
Engine performance issues often show through specific symptoms. Listen for unusual sounds like ticking or knocking, which can mean engine damage. These sounds are common during startup or when you accelerate.
Keep an eye on your dashboard lights. The check engine light, oil pressure warning, or temperature gauge can signal big problems. Also, notice how your truck feels while driving.
Look for changes in power, rough idling, or hard starts. If your engine runs roughly at idle or has trouble keeping RPMs steady, it might be failing.
Step-by-Step Engine Diagnostic Process
Begin by checking your engine oil level and condition. Low oil or metal particles in the oil can mean serious damage. Camshaft failure often leaves metal shavings in the oil system.
Use an OBD-II scanner to read trouble codes. These codes help pinpoint system failures and narrow down the problem area. Always document all codes before clearing them.
Do a compression test on all cylinders. Uneven readings suggest internal damage. This test can reveal problems with pistons, rings, or valves that other tests might miss.
Engine Repair Solutions and Maintenance Tips
V8 engine troubles often need a pro to fix, like internal component failures. Camshaft failure requires taking the engine apart and can cost a lot to repair.
Prevent many engine problems with regular maintenance. Change your oil every 5,000 miles with the right grade. Also, replace air filters often to keep air flowing well to your engine.
Keep an eye on coolant levels and change it as needed. Overheating can cause serious damage that’s expensive to fix. Fix small problems quickly to avoid big failures.
Brake System Problems: Inspection and Repair Methods
Toyota Tundra brake problems often start with subtle warning signs. Your truck’s brake system works hard to stop thousands of pounds safely. Regular brake inspections and prompt repairs are essential for your safety and the safety of others on the road.
The 2008-2010 Tundra models experienced significant brake booster failures. These problems caused repair costs between $600 and $1,200. Early detection is key for your wallet.
Spotting Warning Indicators
Your Tundra will give you clear signals when brake booster issues or other problems develop. A spongy pedal feel is often the first sign something’s wrong. When you press the brake pedal, it should feel firm and responsive.
Watch for increased stopping distances during normal driving. If your truck takes longer to stop than usual, this indicates serious brake wear or system problems. You might also notice reduced brake response, specially when coming to a complete stop.
Listen for unusual sounds like grinding, squealing, or clicking when braking. These noises often signal worn brake pads or damaged components that need immediate attention.
Complete System Inspection Process
Start your brake system inspection by checking the brake fluid level in the master cylinder reservoir. Low fluid levels can indicate leaks or worn brake pads that need replacement.
Examine your brake lines for signs of corrosion, cracks, or fluid leaks. Pay special attention to connection points where lines meet calipers and the master cylinder. Any signs of brake system failure require immediate professional attention.
Check your brake pads through the wheel spokes if possible. Most pads should have at least 1/4 inch of material remaining for safe operation.
Component Replacement Guide
Brake component replacement on your Tundra requires specific tools and safety precautions. Always use jack stands when working under your truck, and never rely on just a jack for support.
Replace brake pads in complete axle sets to maintain even braking performance. Mixing old and new pads can cause uneven wear and reduced stopping power. Professional installation ensures proper torque specifications and safety.
For complex repairs like brake booster replacement, consider professional service. The cost of proper brake component replacement is always less than the potentially dangerous consequences of brake failure.
Electrical System Malfunctions: Diagnosis and Fixes
Your Toyota Tundra’s electrical system controls everything from engine performance to dashboard displays. Toyota Tundra electrical problems were common in 2012 models. Owners faced oxygen sensor malfunctions and navigation system failures, leading to expensive repairs.
Modern truck electrical systems are complex. A single malfunction can trigger many warning lights. Understanding these systems helps you fix problems before they get worse.
Recognizing Electrical Warning Signs
Dashboard warning lights are the first sign of electrical trouble. The check engine light, ABS warning, and airbag indicators often point to sensor issues, not mechanical problems.
Other signs include flickering interior lights, intermittent radio operation, and power window malfunctions. Navigation system freezing was a big issue in 2012 Tundra models, often needing a full system reset.
Step-by-Step Electrical Testing Process
Start your electrical system diagnosis with a visual check of battery terminals and wiring harnesses. Corrosion and loose connections are common causes of many electrical problems.
Use a digital multimeter to test battery voltage. It should read 12.6 volts when the engine is off. Test the alternator output by measuring voltage while the engine runs. It should show 13.5 to 14.5 volts.
Check fuses using the owner’s manual diagram. Replace any blown fuses and find the cause to avoid future failures.
Effective Electrical Repair Solutions
Sensor failures often need a complete replacement, not repair. High-mileage Tundras often see failures in oxygen sensors, mass airflow sensors, and throttle position sensors.
For navigation system issues, try disconnecting the battery for 15 minutes to reset it. If problems continue, software updates from Toyota dealerships can fix compatibility issues.
Ground wire problems can cause strange electrical issues. Clean all ground connections with wire brushes and apply dielectric grease to prevent corrosion.
Suspension and Steering Concerns: Complete Repair Guide
Suspension and steering problems in Toyota Tundra vehicles can affect safety and ride quality. These systems keep your truck stable and easy to control. Toyota issued a recall for 533,000 trucks and SUVs because of faulty lower ball joints.
Failed components can lead to losing control of your vehicle. The lower ball joint recall shows how serious these issues are. Knowing the warning signs is key to staying safe.
Recognizing Suspension Problem Symptoms
Your Tundra will show signs when suspension parts fail. Look out for these common signs:
- Excessive bouncing after hitting bumps or dips
- Pulling to one side while driving straight
- Uneven tire wear patterns on your wheels
- Clunking or rattling noises from underneath
- Nose diving when braking hard
These problems often start slowly. Notice any changes in how your truck feels and handles.
Step-by-Step Steering System Diagnosis
Diagnosing steering issues needs a step-by-step approach. Start with these basic checks:
- Test steering wheel play by turning it gently while parked
- Check for fluid leaks under the power steering reservoir
- Listen for whining noises when turning the wheel
- Feel for vibrations through the steering wheel while driving
Get a professional inspection if you notice steering issues that affect control. Don’t wait to get help with serious symptoms.
Suspension and Steering Component Repairs
Most suspension repairs need special tools and knowledge. Ball joints, struts, and steering linkages often fail in Tundras.
You can do some maintenance yourself, like checking tire pressure. But, safety-critical repairs like ball joint replacement should be done by experts.
Regular maintenance can prevent many issues. Have your suspension and steering systems checked every 12,000 miles to catch problems early.
Cooling System Failures: Prevention and Solutions
Your Toyota Tundra’s cooling system keeps your V8 engine cool. Many owners face Toyota Tundra cooling system problems that can cost a lot to fix. Regular checks and quick action can save you from big repairs.
The cooling system keeps your engine at the right temperature. If it fails, your engine could get damaged. Knowing how it works helps you spot problems early.
How to Spot Overheating Warning Signs
Spotting overheating issues early can save your engine. Look out for these signs while driving.
A red temperature gauge means you need to act fast. Steam or white smoke from under the hood is a sign of boiling coolant. Sweet-smelling coolant usually means a leak.
Some owners find pink coolant, which can mean contamination. This might also affect your transmission, so get it checked by a pro.
Complete Cooling System Inspection Guide
Regular checks can stop most cooling system problems. Start by checking the coolant when the engine is cold. Look for leaks around hoses, connections, and the radiator.
Check hoses for damage and the radiator cap for leaks. Test the thermostat by watching how long it takes for the engine to warm up.
Radiator and Coolant System Repairs
Radiator problems like clogs, leaks, and fan failures are common. Clean the radiator fins often to keep air flowing. Replace damaged hoses right away to avoid sudden failures.
For coolant system maintenance, flush it every 60,000 miles. Use only Toyota-approved coolant to avoid corrosion and keep your warranty valid.
| Component | Inspection Frequency | Common Issues | Replacement Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Radiator | Every 6 months | Leaks, clogs | $400-$800 |
| Water Pump | Every 12 months | Bearing failure | $300-$600 |
| Thermostat | Every 24 months | Stuck closed/open | $100-$250 |
| Coolant Hoses | Every 6 months | Cracks, bulges | $50-$150 |
Fuel System Problems: Troubleshooting and Maintenance
When your Toyota Tundra shows fuel delivery problems, quick action saves money and time. Toyota Tundra fuel system problems can hurt engine performance and daily driving. Knowing these issues helps fix them early, avoiding costly repairs.
Your fuel system has many parts working together. The fuel pump, filter, injectors, and gauge are all key. Many Tundra owners face fuel gauge problems where the gauge shows more fuel than there is.
Identifying Fuel System Symptoms
Several signs point to fuel system trouble. Engine hesitation when accelerating often means fuel pump issues or clogged filters. You might also notice rough idling or hard starts.
Fuel gauge issues show up as erratic readings or stuck needles. Some owners see gauges that say full when the tank is almost empty. Strange noises from the fuel tank area also hint at pump problems.
Diagnosing Fuel Pump and Filter Issues
Testing your fuel system needs basic tools and safety. Start by checking fuel pressure with a gauge at the rail. Normal pressure is between 44-50 PSI for most Tundra models.
Listen for the fuel pump’s humming sound when you turn the key to “on”. A silent pump often means it’s failed. Check fuel filters for clogs by examining flow rate and fuel color.
Step-by-Step Fuel System Maintenance
Regular fuel system maintenance prevents many common issues. Replace fuel filters every 30,000 miles or as your owner’s manual suggests. Use quality fuel from reputable stations to reduce contamination.
| Maintenance Task | Frequency | Cost Range | Difficulty Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fuel Filter Replacement | 30,000 miles | $25-$60 | Moderate |
| Fuel Pump Inspection | 60,000 miles | $15-$30 | Easy |
| Fuel Injector Cleaning | 45,000 miles | $50-$150 | Professional |
| Fuel System Flush | 100,000 miles | $100-$200 | Professional |
Keep your fuel tank above quarter-full to prevent pump overheating. This simple habit extends pump life and keeps your fuel system in good shape.
Exhaust System Issues: Detection and Repair Methods
Toyota Tundra exhaust problems show up as odd sounds and less engine power. The exhaust system is key to removing harmful gases and keeping your truck running well. When it fails, you’ll hear and feel the difference right away.
Exhaust manifold failure is a big problem, with over 261 Tundra owners facing it. This issue makes a ticking sound, louder when the engine is cold. Spotting these signs early can prevent bigger issues.
Recognizing Warning Signs
Listen for odd sounds from your engine or under the truck. A ticking sound when starting cold often means manifold trouble. Loud rumbling or hissing while driving is another sign.
Look out for lower fuel efficiency and less engine power. Exhaust system noise gets louder with time, and during acceleration. Black smoke or strong odors inside mean you need to act fast.
Check your dashboard for warning lights. The check engine light often comes on for exhaust issues.
Inspection Methods
Begin by looking under the truck. Check for rust, holes, or loose connections in the exhaust pipes. Focus on where pipes meet.
Examine the exhaust manifold with the engine running. Listen for air leaks or odd sounds. Use a flashlight to find cracks or damaged gaskets.
Test the system by briefly covering the tailpipe with a rag. A good exhaust system will show back pressure. Weak pressure means a leak.
Repair Solutions
Small leaks might just need gasket or pipe fixes. These fixes are often cheap and quick. But, exhaust component replacement is needed for bigger damage.
Fixing manifolds can range from replacing gaskets to installing a new one. Mechanics say replacing is better for lasting results. The repair time varies based on how easy it is to get to.
Think about getting aftermarket parts for better durability. High-quality parts last longer and might perform better for your driving style.
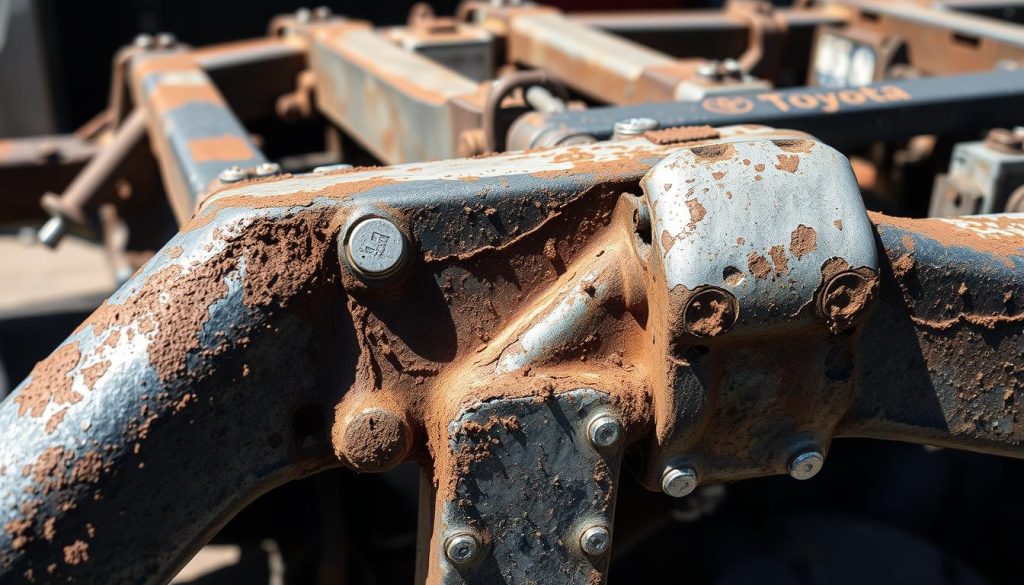
Body and Frame Problems: Inspection and Prevention
Many Toyota Tundra owners face corrosion problems, mainly in areas with lots of salt. These issues were common in the first models from 2000-2006. The Toyota Tundra frame rust problem caused expensive repairs and safety worries for thousands.
Frame damage often starts from the inside, making it hard to spot early. Road salt makes this damage worse. Toyota tried to fix the problem with recalls and extended warranties, but not all trucks were covered.
Identifying Rust and Corrosion Issues
Look for rust flakes around where the frame meets other parts. Surface rust looks like brown or orange spots on metal. Also, check for holes or soft spots that show advanced corrosion.
Listen for unusual sounds while driving. Creaking or groaning might mean the frame is weak. Check the truck bed area where rust often shows up.
Frame Inspection Techniques and Safety Tips
Wear proper safety gear when checking under your truck. Frame inspection techniques need good light and careful checks of all frame rails. Look closely at areas where brackets and parts attach to the frame.
Don’t ignore any structural worries. If you find big rust damage, get a pro to inspect it. Frame problems can affect your truck’s safety and how it handles.
Body Repair and Prevention Solutions
Body rust prevention starts with regular washing, more so in winter. Use protective coatings on areas prone to rust before it starts.
| Repair Type | Cost Range | Timeline | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surface Treatment | $200-$500 | 1-2 days | Good for early rust |
| Frame Reinforcement | $1,500-$2,500 | 3-5 days | Moderate damage |
| Frame Replacement | $3,000-$5,000 | 1-2 weeks | Severe corrosion |
Professional repairs can cost between $2,500 and $3,500 for full frame work. Prevention is much cheaper than fixing, so regular care is key for keeping your truck in good shape.
Interior and Accessory Malfunctions: Quick Fixes
Toyota Tundra interior problems often show up as dashboard issues, seat control failures, and electronic accessory problems. These issues can be small annoyances or serious safety risks that need quick action.
Some Tundra models have had temperature seat switch malfunctions that could start fires. Radio volume knob failures and breakdowns in dashboard components also affect the driving experience.
Spotting Interior Issues Early
Look out for these common signs of accessory malfunctions:
- Seat controls that feel hot or smell like burning
- Radio volume knobs that stick or don’t work
- Dashboard lights that flicker or stay on
- Climate control buttons that don’t work
- Power outlet failures that stop devices from charging
Simple Troubleshooting Methods
Begin with simple checks before calling a pro. Check fuse boxes for blown fuses related to interior systems. Clean electrical connections with contact cleaner to remove corrosion.
Test each part slowly and listen for odd sounds. Take photos of dashboard issues to help mechanics find the problem.
DIY Interior Component Fixes
Many repairs don’t need special tools. Use the owner’s manual fuse diagram to replace blown fuses. Clean sticky buttons with electronics-safe cleaners.
For seat switch problems, disconnect the battery right away and avoid heated seats until fixed. Simple knob swaps often fix radio volume problems without expensive parts.
If dashboard issues keep happening after basic checks, get a pro’s help. They ensure safety and prevent more damage to electrical systems.
Toyota Tundra Problems by Model Year: What to Expect
Knowing which Toyota Tundra years to avoid can save you a lot of money and stress. Each Tundra generation has had its own set of problems, from rust to transmission issues. It’s smart to check model year problems before buying.
The Toyota Tundra has gone through three main changes from 2000 to now. Each update brought new features but also new issues. Knowing these can help you make a smart choice, whether buying used or understanding your truck’s issues.
2007-2013 First Generation Common Issues
The first Tundra generation had big problems that make some years bad for buyers. The worst Tundra years were 2007, 2008, and 2010 because of many mechanical failures.
Frame rust was a big problem starting in 2005, leading to many recalls. The 2007 model had air injection pump failures and weak transmissions. These issues cost a lot to fix, often more than the truck was worth.
The 2008 Tundra had camshaft failures and brake booster problems. Many owners also reported engine knock and wear. The 2010 model had oil consumption and air injection system failures.
“The 2007-2010 Tundras had so many problems that Toyota extended warranties multiple times to address customer complaints.”
But, the 2013 model year was a big improvement. Toyota fixed many reliability issues, making it a reliable year.
2014-2021 Second Generation Problem Areas
The second generation was better than the first. The best Tundra years were 2015 and 2019, with high reliability and fewer warranty claims.
Early second-generation models had some issues. The 2014 model had minor electrical and sensor problems. These were less severe than the first generation’s issues but needed fixing.
The 2016-2018 models had mixed results. While they were mechanically reliable, some owners had infotainment system and electrical issues. These didn’t affect driving but were annoying.
| Model Year | Reliability Rating | Common Issues | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2007-2008 | Poor | Frame rust, transmission, camshaft | Avoid |
| 2010-2012 | Below Average | Oil consumption, electrical | Caution |
| 2013-2015 | Good | Minor issues only | Recommended |
| 2019-2021 | Excellent | Very few complaints | Highly Recommended |
2022+ Third Generation Early Concerns
The newest Tundra generation has the latest technology. Early reports show it avoids the big model year problems of earlier models.
Initial data for 2022-2024 models looks good. Most issues are minor software updates, not mechanical failures. The hybrid powertrain has also done well in tests.
Some owners have reported minor infotainment glitches and adaptive cruise control needs. These are usually fixed with software updates, not hardware changes. Overall, the third generation seems to keep Toyota’s reliability trend.
The 2022 and newer models use Toyota’s latest manufacturing and quality control. Early reliability ratings suggest they will be among the most reliable Tundras ever.
Conclusion
Your Toyota Tundra can last for many years if you take care of it. Knowing which model years to avoid is key. Stay clear of the 2005, 2007, 2008, 2010, and 2012 models due to frequent issues.
Instead, look for the 2013, 2015, 2019, and 2022-2024 models. These years offer better reliability and fewer problems.
Regular maintenance is essential. Check your transmission fluid and air injection system. Also, watch for any early warning signs. These steps can prevent expensive repairs later.
Spotting problems early saves money and stress. Pay attention to your truck’s sounds, lights, and performance. Quick action can stop small issues from becoming big ones.
For the best Tundra experience, choose the right model year, maintain it well, and fix problems early. This approach keeps your truck reliable and valuable.
With this advice, you can make smart choices about your Toyota Tundra. Proper care will reward you with years of dependable service.
FAQ
What are the most common Toyota Tundra problems across all model years?
Toyota Tundras often face issues like transmission problems, air injection pump failures, and engine issues. Brake and electrical system failures are also common. Frame rust is a big problem in older models. Each year has its own set of issues.
Which Toyota Tundra model years should I avoid when buying used?
Stay away from 2007-2008, 2009-2010, and 2014-2015 models. These years have major problems like transmission and frame rust issues. The 2007 model is the worst due to multiple serious issues.
How can I tell if my Toyota Tundra has transmission problems?
Look for harsh shifting, delayed engagement, and slipping gears. Unusual noises and fluid leaks are also signs. If you see these in 2007-2010 models, get it checked fast.
What is the air injection pump problem in Toyota Tundras?
Second-generation Tundras (2014-2021) often have air injection pump failures. This affects the emissions system. Symptoms include check engine lights and rough idling. Replacing the pump can cost
FAQ
What are the most common Toyota Tundra problems across all model years?
Toyota Tundras often face issues like transmission problems, air injection pump failures, and engine issues. Brake and electrical system failures are also common. Frame rust is a big problem in older models. Each year has its own set of issues.
Which Toyota Tundra model years should I avoid when buying used?
Stay away from 2007-2008, 2009-2010, and 2014-2015 models. These years have major problems like transmission and frame rust issues. The 2007 model is the worst due to multiple serious issues.
How can I tell if my Toyota Tundra has transmission problems?
Look for harsh shifting, delayed engagement, and slipping gears. Unusual noises and fluid leaks are also signs. If you see these in 2007-2010 models, get it checked fast.
What is the air injection pump problem in Toyota Tundras?
Second-generation Tundras (2014-2021) often have air injection pump failures. This affects the emissions system. Symptoms include check engine lights and rough idling. Replacing the pump can cost $1,500-$3,000 at dealerships.
Are Toyota Tundra brake problems serious safety concerns?
Yes, brake issues are very serious. Look out for premature wear, pulsation, leaks, and warning lights. Some years have had recalls. Any brake problem needs immediate attention.
How do I check for frame rust on my Toyota Tundra?
Check for rust spots, flaking metal, and holes on the frame. Look at areas around the spare tire and rear cross members. First-generation Tundras (2007-2013) are most prone to rust.
What engine problems are common in Toyota Tundras?
Tundras may have camshaft timing issues, carbon buildup, oil consumption, and cooling system failures. The 5.7L V8 engine has camshaft problems in some years. The 4.6L V8 has fewer issues.
How much do Toyota Tundra repairs typically cost?
Repair costs vary. Transmission rebuilds cost $3,000-$5,000. Air injection pump replacement is $1,500-$3,000. Engine repairs can be $500-$8,000. Brake repairs cost $300-$1,500. Regular maintenance can help save money.
Are there any Toyota Tundra recalls I should know about?
Yes, Toyota has recalled Tundras for frame rust, brake issues, airbag problems, and more. Check your VIN on the Toyota or NHTSA website for recalls.
What’s the most reliable Toyota Tundra model year?
The most reliable years are 2011-2013, 2016-2019, and 2022+. These years have fewer problems and better quality than earlier models.
How can I prevent common Toyota Tundra problems?
Regular maintenance is key. Change oil, service the transmission, and check brakes and cooling systems. Use quality fluids and follow Toyota’s schedule. Early detection and maintenance can prevent costly repairs.