Toyota Engine Misfire: Symptoms, Causes, and Repairs
Is your car running rough or losing power? You might have a Toyota engine misfire. This issue happens when one or more cylinders don’t ignite right during combustion.
A misfiring cylinder messes with your car’s smooth drive. You’ll see engine misfire symptoms like rough idling, slow acceleration, and bad fuel economy. The check light on your dashboard will also turn on.
Knowing these signs is key to fixing problems early. A pro Toyota misfire diagnosis with special scanners can find the exact cylinder issue.
This guide covers all you need to know about spotting, diagnosing, and fixing these issues. It’s for anyone driving a Camry, Corolla, or Prius. The info here will help you drive safely again.
Key Takeaways
- Misfires cause rough idling, power loss, and reduced fuel efficiency
- Check lights typically activate when combustion problems occur
- Professional diagnostic tools help identify specific cylinder issues
- Early detection prevents more expensive repairs
- All vehicle models can experience these combustion problems
Understanding Engine Misfires in Toyota Vehicles
A Toyota engine misfire is when the combustion sequence breaks down. This happens when one or more cylinders don’t ignite the fuel-air mix right. Knowing the Toyota misfire causes helps you catch issues early and keep your car running well.
Your Toyota engine works like a well-choreographed dance. Each cylinder fires in a specific order for smooth power. It needs the right fuel-air mix, compression, and spark timing.
When engine combustion problems happen, the dance gets disrupted. A cylinder might not burn fuel well or not at all. This causes symptoms like rough idling and losing power.
Even the most reliable engines can develop misfires due to normal wear and component aging over time.
Toyota engines are known for their reliability thanks to precise engineering. But, they’re not immune to wear and tear. Common issues include worn spark plugs, clogged fuel injectors, and air intake leaks.
The effect on Toyota engine performance is clear when misfires happen. Your engine works harder to make up for lost power. This can lead to more fuel use and damage to other parts.
Quick action is essential when you think there’s a misfire. Ignoring it can make the problem worse and cost a lot to fix. Knowing how your engine should work helps you see why fixing it fast is important.
Recognizing Toyota Engine Misfire Symptoms
Spotting engine misfire symptoms early can prevent costly repairs. Your Toyota alerts you to engine issues. Knowing these signs helps you fix problems before they get worse.
Toyota owners can notice engine problems by observing changes in their car’s behavior. When cylinders misfire, your car shows clear signs. These signs start small but grow over time.
Engine Performance Warning Signs
Engine misfires change your Toyota’s performance. A common sign is rough idling, causing your car to shake or vibrate. This often happens at red lights or when parked.
Acceleration problems also indicate engine issues. Your engine may feel slow when you press the gas pedal. Hills and highway merging become harder as your Toyota struggles to speed up.
Poor fuel economy is another sign of engine misfires. You’ll need to fill up more often. This is because your engine works harder to make up for misfiring cylinders.
Dashboard Indicator Lights and Error Codes
The check engine light alerts you to engine problems. This light turns on when your car’s computer detects irregular engine behavior. Modern Toyotas store specific codes to identify misfiring cylinders.
Some Toyotas show additional warning lights, like engine temperature or oil pressure alerts. Your dashboard becomes a center for communication during engine issues.
OBD-II scanners can read these error codes to find exact misfire locations. Common codes include P0300 for random misfires and P0301-P0308 for specific cylinder misfires. These codes help mechanics diagnose problems fast.
Physical Symptoms While Driving
Driving with engine misfires causes noticeable symptoms. You might feel your car jerking or stumbling during acceleration. It may feel like it’s hesitating or losing power.
Unusual sounds often come with misfire symptoms. You might hear popping, backfiring, or irregular engine rhythms. These sounds mean fuel isn’t burning right in one or more cylinders.
Exhaust symptoms also give visual clues about engine problems. Black smoke from your tailpipe suggests a rich fuel mixture. Strong fuel odors around your vehicle mean unburned gasoline is escaping through the exhaust.
Starting difficulties become more common as misfires worsen. Your Toyota may take longer to start or need multiple tries. Cold weather makes these starting problems worse.
How Engine Misfires Impact Toyota Performance
Engine misfires lead to many problems that affect your Toyota’s performance. When cylinders don’t fire right, your car doesn’t run smoothly. This makes driving every day a challenge.
Your Toyota might feel slow when you try to speed up. It might also hesitate when you press the gas. This makes it hard to merge onto highways because your engine doesn’t have enough power.
Toyota fuel efficiency drops a lot with misfires. Your engine works harder, using more fuel. This means you’ll need to fill up more often and spend more on gas.
Ignoring misfires can cause serious engine damage. Engine damage happens when cylinders don’t fire right. This wears out parts like pistons and valves.
Your catalytic converter is also at risk. It can get too hot and fail, costing over $1,000 to replace. Catching misfires early is key to avoiding this expensive fix.
Emissions problems also arise from misfires. Your car’s exhaust emissions increase, leading to failed emissions tests. Many places require passing these tests to register your vehicle.
| Performance Impact | Immediate Effects | Long-term Consequences | Estimated Repair Costs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power Loss | Sluggish acceleration | Complete engine failure | $3,000 – $8,000 |
| Fuel Economy | 15-25% decrease in MPG | Ongoing fuel waste | $500+ annually |
| Emissions | Failed emissions tests | Catalytic converter damage | $800 – $1,500 |
| Engine Components | Rough idle and vibration | Internal engine damage | $2,000 – $5,000 |
Waiting too long to fix misfires can cost a lot. What seems like a simple fix can turn into a big problem. Fixing it early saves money and keeps you safe.
Driving with misfires also hurts other parts of your car. Your transmission works harder, which can shorten its life. It also puts extra stress on your car’s electrical system, leading to more problems.
Emissions problems from misfires pollute the environment. They can also lead to fines in places with strict air quality rules. If your car fails emissions tests too many times, you might face penalties.
Knowing how misfires affect your car shows why fixing them quickly is important. The next step is figuring out how to find and fix the problem.
Step 1: Performing Initial Toyota Engine Misfire Diagnosis
Before you start fixing your Toyota’s misfiring engine, you need to do a full diagnosis first. This step is key to saving time and money. It helps you find the exact problem instead of just guessing. Proper diagnosis prevents unnecessary part replacements and fixes the real cause of the misfire.
Start by doing a visual check and then move to electronic tests. This order helps you find obvious problems first. Then, you can tackle the more complex ones.
Visual Inspection Checklist
Start by looking at the engine bay carefully. Check for signs of damage or wear that might cause the engine to misfire. Often, you can fix problems right away with this initial check.
Here are some key things to check:
- Ignition coils – Look for cracks, corrosion, or loose connections
- Spark plug wires – Check for fraying, burns, or damaged insulation
- Vacuum hoses – Inspect for cracks, splits, or loose fittings
- Engine fluids – Look for oil or coolant leaks affecting performance
- Air filter housing – Ensure proper sealing and connection
Write down any problems you find. Take photos if necessary to help with repairs later.
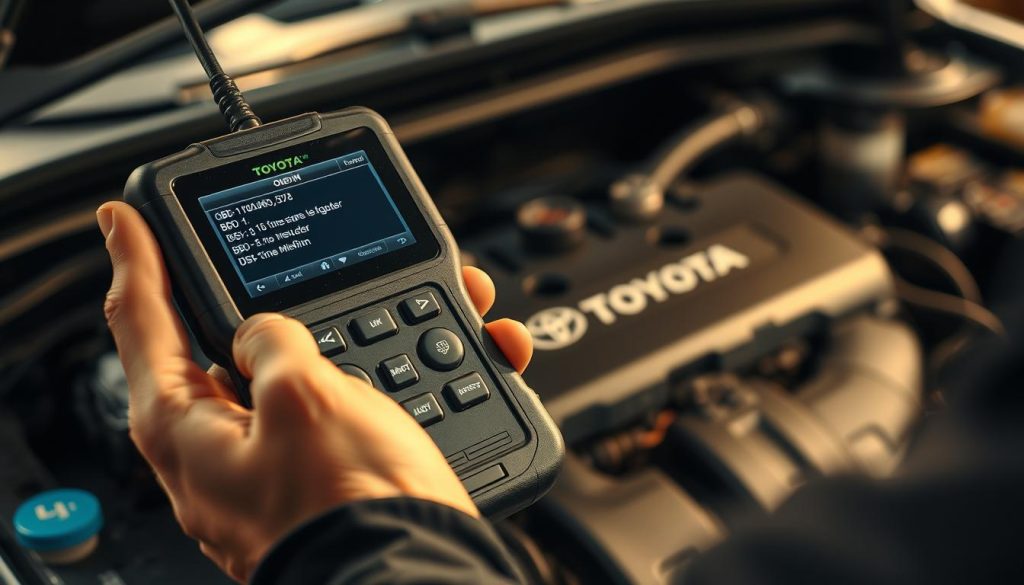
Connecting OBD-II Scanner
Every Toyota made after 1996 has an OBD-II system. This system checks engine performance. Using an OBD-II scanner gives you important info on misfiring cylinders and possible causes.
Find the diagnostic port under your dashboard, near the driver’s left knee. The port is usually rectangular with 16 pins. Plug in your scanner and turn on the ignition without starting the engine.
Most scanners will connect to your Toyota’s system automatically. Wait for the connection confirmation before reading codes.
Reading and Recording Error Codes
Toyota diagnostic codes guide your repair. These codes tell you exactly which cylinders are misfiring and often show the underlying cause.
Here are some common misfire codes:
- P0300 – Random multiple cylinder misfire detected
- P0301-P0308 – Specific cylinder misfire (cylinder 1-8)
- P0171/P0174 – System too lean (fuel-related misfires)
- P0420 – Catalytic converter efficiency (misfire-related damage)
Write down all codes and their descriptions. Don’t clear the codes yet – you’ll need them for reference. Some codes may only appear when the engine runs under certain conditions, so record everything.
Use your visual inspection findings and diagnostic codes to understand your Toyota’s misfire problem. This info helps you plan your next steps and decide which parts to test first.
Step 2: Gathering Essential Diagnostic Tools
Having the right automotive tools makes fixing engine misfires easier. It turns a frustrating task into a precise one. You need a full set of tools for both basic and advanced tests to find Toyota engine misfire causes.
The right diagnostic equipment can save you time and money. It ensures you get accurate results quickly.
Basic Equipment Requirements
Start with a reliable OBD-II scanner. It reads and clears error codes from your Toyota’s computer. This tool points you to the misfire’s source.
A digital multimeter is very useful. It tests electrical parts like ignition coils and checks voltage and spark plug wire continuity. Without it, finding electrical issues is hard.
You’ll also need a socket set, screwdrivers, and needle-nose pliers for removing and installing parts. A spark plug gap gauge is key for new plugs. A compression tester finds serious engine problems that might cause misfires.
- OBD-II scanner for code reading
- Digital multimeter for electrical testing
- Socket set and basic hand tools
- Spark plug gap gauge
- Compression tester
Advanced Testing Instruments
Professional-grade scan tools stream live data. They show engine parameters in real-time, catching problems missed by basic scanners.
An oscilloscope checks ignition system waveforms. It finds electrical issues that multimeter testing can’t. This tool is key for spotting ignition coil and spark plug problems.
Fuel pressure gauges measure fuel delivery issues. Smoke machines show vacuum leaks by introducing smoke into the intake system. These tools are essential for complex misfire problems.
While these tools are expensive, they’re worth it for accurate first-time diagnosis. They give detailed info needed for quick fixes.
Think about your skill level and budget when choosing tools. Start with basics and add more as you get better.
Step 3: Testing Ignition System Components
Testing the ignition system is key to your Toyota engine’s health. It checks three main parts that work together to spark your engine. If any part fails, your engine might misfire and run poorly.
Your Toyota’s ignition system must work well to avoid engine damage. Testing these parts carefully helps find problems early. This method saves time and ensures you get the right diagnosis.
Inspecting Spark Plugs for Wear
Spark plug inspection tells you a lot about your engine. Take out each spark plug and label them by cylinder. This makes it easier to see which cylinders have issues.
Look at the electrode and ceramic insulator for damage. Normal spark plugs have light brown or gray on the electrodes. Black or sooty buildup means you need to fix the fuel mixture.
White or blistered electrodes mean the fuel mix is too lean or the engine is overheating. Worn electrodes with big gaps cause weak sparks and misfires. Replace any spark plugs that look unusual or damaged.
Testing Ignition Coil Performance
Testing the ignition coil involves looking and measuring. Modern Toyotas have a coil for each cylinder, making it easier to find problems. Check each coil for cracks, corrosion, or heat damage.
Use a digital multimeter to check resistance. Compare your numbers to Toyota’s specs for your engine. Coils that don’t match should be replaced right away.
Weak coils cause misfires that get worse over time. Testing coil performance stops unexpected breakdowns and keeps your engine running well. Keep a record of your resistance readings.
Checking Spark Plug Wire Condition
Spark plug wires carry high voltage from the distributor to each plug. These cables are key in older Toyotas. Check each wire for cracks, burns, or worn insulation.
Look for carbon marks that show electrical arcing. Damaged wires cause misfires, worse in wet weather. Use a multimeter to test wire resistance and make sure it’s conducting well.
Replace any wires that look bad or have high resistance. Good spark plug wires improve ignition and prevent future problems. Keeping wires in good shape helps your ignition system last longer.
Step 4: Diagnosing Fuel System Problems
The fuel system diagnosis process helps find out if injector problems, pressure issues, or fuel quality concerns cause your Toyota’s misfires. Your engine needs the right amount of clean fuel at the right pressure to run smoothly. If any part of this system fails, misfires happen quickly.
Modern Toyota fuel injection systems are complex but sensitive to contamination and wear. Fuel injector problems often develop gradually, making early detection key to preventing costly repairs. The diagnostic process involves three main areas that work together to ensure proper fuel delivery.
Testing Fuel Injector Function
Start your injector testing by checking for external fuel leaks around each injector. Look for wet spots, fuel stains, or strong gasoline odors that indicate worn O-rings or damaged injector bodies. These signs often point to immediate fuel injector problems that need attention.
Listen to each injector while the engine runs using a mechanic’s stethoscope or long screwdriver. Place the tool against each injector body and listen carefully. Properly working injectors make a consistent clicking sound as they open and close rapidly.
For thorough testing, you can remove injectors to check their spray patterns and flow rates. This requires special equipment and careful fuel system handling. Always relieve fuel pressure before disconnecting any fuel lines to prevent dangerous fuel spray.
A properly functioning fuel injector should produce a fine, cone-shaped spray pattern when tested outside the engine.
Checking Fuel Pressure Levels
Fuel pressure testing reveals whether your fuel pump and pressure regulator work correctly. Low pressure causes lean misfires, while high pressure creates rich conditions that foul spark plugs. Both situations lead to poor engine performance.
Connect a fuel pressure gauge to your Toyota’s fuel rail test port. Measure both static pressure with the engine off and running pressure at idle. Compare these readings to Toyota’s specifications for your specific engine model.
Perform a pressure hold test by turning off the engine and watching the gauge. Pressure should hold steady for several minutes. Rapid pressure drop indicates fuel pump problems or internal fuel leaks that need repair.
| Engine Type | Static Pressure (PSI) | Running Pressure (PSI) | Minimum Hold Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4-Cylinder | 44-50 | 38-44 | 5 minutes |
| V6 Engines | 44-50 | 38-44 | 5 minutes |
| Hybrid Systems | 50-60 | 44-54 | 10 minutes |
| Turbo Models | 58-65 | 52-58 | 5 minutes |
Inspecting Fuel Quality
Poor fuel quality causes surprising numbers of misfire problems in Toyota vehicles. Water contamination, dirt particles, or old fuel can clog injectors and create combustion issues. Fuel system diagnosis must include checking what’s actually in your tank.
Remove a small fuel sample from the tank using a clean container and siphon pump. Fresh gasoline appears clear and smells like typical gasoline. Contaminated fuel may look cloudy, have visible particles floating in it, or smell sour and stale.
Water contamination shows up as a separate layer at the bottom of your sample container. Even small amounts of water cause injector problems and poor combustion. If you find water contamination, drain the entire fuel system and refill with fresh gasoline.
Check fuel age if your Toyota sits unused for extended periods. Gasoline degrades over time, forming gum and varnish deposits that clog fuel injectors. Fuel older than three months often causes performance problems in modern fuel injection systems.
Consider using a fuel system cleaner if you suspect minor contamination but find no major issues. These additives help dissolve deposits and restore proper injector function without requiring complete system disassembly.
Step 5: Examining Air Intake System Issues
Air intake problems can quietly harm your Toyota’s performance. They disrupt the air-fuel mixture needed for smooth combustion. Your engine’s computer needs accurate airflow measurements to deliver the right fuel. When the air intake system fails, misfires become inevitable.
The air intake system has many parts that work together. Vacuum hoses, intake manifolds, and sensors must all work right. Even small problems can cause big performance issues.
Detecting Vacuum Leaks
Vacuum leaks let unmetered air into your engine. This creates a lean fuel mixture that causes rough idling and misfires. These leaks often start small and are hard to notice at first.
Start by looking at all vacuum hoses visually. Check for cracks, splits, or loose connections around the intake manifold. Rubber hoses near the engine block are prone to damage from heat.
To find leaks, use the propane enrichment method while the engine idles. Spray small amounts of propane near suspected leak points. If the engine RPM changes, you’ve found a leak.
A safer way is to use carburetor cleaner spray. Spray suspected areas while the engine idles. If engine speed changes, you’ve found a leak.
Testing Mass Airflow Sensor
The mass airflow sensor measures air volume and sends data to your Toyota’s engine computer. When it fails, your engine gets the wrong fuel delivery commands. This leads to consistent misfires across multiple cylinders.
Remove the mass airflow sensor carefully from the air intake tube. Look for dirt, oil contamination, or damage on the sensing elements. Clean elements are silver or platinum colored.
Use specialized MAF sensor cleaner to clean contamination. Never touch the sensing elements with your fingers or tools, as this can cause permanent damage.
Test the sensor’s electrical output with a digital multimeter. Connect the meter to the sensor’s signal wire while the engine runs. Compare voltage readings to Toyota’s specs for your engine model.
| Detection Method | Equipment Needed | Safety Level | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Flashlight, Mirror | High | Moderate |
| Propane Enrichment | Propane Torch | Medium | High |
| Carburetor Cleaner Spray | Spray Can | High | High |
| Smoke Machine Testing | Professional Equipment | High | Excellent |
Smoke machine testing is the most thorough way to find vacuum leaks. It pumps harmless smoke through the intake system, making leaks visible. Many repair shops offer this service when DIY methods fail.
Step 6: Replacing Spark Plugs in Toyota Engines
Proper spark plug replacement can greatly improve your Toyota’s performance. It can also fix persistent misfire problems. Modern Toyota engines need the right spark plugs for good combustion and fuel efficiency.
Using the right spark plugs is key. Quality spark plugs made for your Toyota engine will keep it running well for a long time. The wrong plugs can make misfires worse and harm your engine.
Preparing Tools and Replacement Parts
Getting ready is the first step to success. Make sure you have all the tools you need before starting spark plug installation on your Toyota.
You’ll need a spark plug socket, a ratchet handle, extension bars, and a torque wrench. Most Toyotas need torque settings between 15-25 ft-lbs. This is why accuracy is so important.
- Spark plug socket (typically 5/8″ or 13/16″)
- Ratchet and extension bars
- Torque wrench with accurate low-range readings
- Feeler gauges for gap measurement
- Compressed air for cleaning debris
Buy Toyota spark plugs from trusted sources like NGK, Denso, or genuine Toyota parts. Make sure to get the correct part number for your engine model and year. Replacing all plugs at once ensures even performance in all cylinders.
Removing Worn Spark Plugs Safely
Be patient when removing spark plugs to avoid damage. Let your engine cool down first. Hot parts can burn you and make removal hard.
Take off any engine covers or air intake parts to get to the spark plugs. Use compressed air to clean out debris from each well before you start.
“Take your time during spark plug removal. Rushing this step often leads to broken plugs or damaged threads that require expensive repairs.”
Turn each plug counterclockwise slowly and steadily. If it gets hard, stop and use penetrating oil. Never force a stubborn plug, as this can strip the aluminum threads in your cylinder head.
Installing New Spark Plugs Correctly
Installing spark plugs right is key for good performance and to avoid future issues. Start each new plug by hand, turning clockwise until it seats against the cylinder head.
This method prevents cross-threading, which can damage your engine’s spark plug holes. Once it’s finger-tight, use your torque wrench to get the exact torque listed in your Toyota owner’s manual.
Gap Setting and Torque Specifications
Getting the gap right is important for spark formation and engine performance. Check each new plug’s gap with feeler gauges before you install it.
Most Toyota engines need gaps between 0.028″ and 0.044″, depending on the model. Check your owner’s manual for the exact specs. Wrong gaps can cause weak spark or misfires.
| Engine Type | Gap Specification | Torque Setting |
|---|---|---|
| 4-Cylinder | 0.028″ – 0.031″ | 18 ft-lbs |
| V6 Engines | 0.039″ – 0.043″ | 20 ft-lbs |
| Hybrid Systems | 0.031″ – 0.035″ | 15 ft-lbs |
Apply anti-seize compound sparingly to the threads of new plugs before installation. This makes future removal easier and protects the aluminum cylinder head threads.
Spark plug replacement done right will boost your Toyota’s performance and fix misfire issues. Take a test drive after installation to check if everything is running smoothly.
Step 7: Installing New Ignition Coils
Replacing faulty ignition coils can greatly improve your Toyota’s engine performance. It also fixes persistent misfire problems. This step is key and involves identifying bad coils, removing them correctly, and installing new ones.
Modern Toyotas use individual coils, making replacement easier than older models. This simplifies the ignition coil replacement process.
Identifying Failed Ignition Coils
First, visually inspect all ignition coils in your engine bay. Look for damage like cracked housings, burned connectors, or oil around the bases. These signs often mean coils need to be replaced.
But, some failures are hidden inside. Use a digital multimeter to check each coil’s resistance. Compare these values to Toyota’s specs for your engine. Toyota ignition coils with infinite or zero resistance, or values far off, need to be replaced.
Also, consider the coils’ age and mileage. If one coil fails and others have over 100,000 miles, replace them all. This prevents future problems and keeps your engine running well.
Coil Removal and Installation Process
Always disconnect the battery before starting any ignition system work. This prevents electrical damage. Remove engine covers and any parts blocking the ignition coils.
Disconnect each coil’s electrical connector by pressing the release tab and pulling straight out. Remove the mounting bolts holding each coil, usually one per coil. Lift coils straight up to avoid damaging the spark plug boots.
Check the spark plug boots for cracks or wear. Apply a thin layer of dielectric grease to new coil boots before installation. This prevents moisture and makes removal easier.
Install new coils by reversing the removal process. Push each coil down firmly until it seats completely on the spark plug. Tighten mounting bolts to Toyota’s specified torque values, usually between 7-10 foot-pounds.
Testing New Coil Performance
After installation, reconnect the battery and start your engine. Listen for a smooth idle and test acceleration. The engine should run smoother than before.
Use your OBD-II scanner to check if misfire codes have cleared. Perform coil testing by monitoring live data while the engine runs. New coils should show consistent firing patterns across all cylinders.
Take your Toyota for a test drive to confirm the repair success. Pay attention to acceleration smoothness and overall engine performance. Properly installed new coils will restore your engine’s power and eliminate rough running conditions.
Step 8: Servicing Toyota Fuel Injectors
Fixing fuel injector problems needs a careful plan. This includes cleaning or replacing parts. Toyota fuel injectors work hard, sending the right amount of fuel to each cylinder. If they get dirty or wear out, your engine might misfire.
Today’s Toyota engines need clean fuel injectors to run well. Dirt, carbon, and wear can block fuel flow. This leads to bad fuel mixes and engine issues.
Professional Injector Cleaning Methods
Professional fuel injector cleaning is the best way to fix injectors. They use special tools to test and clean each injector outside the engine.
They use solvents to clean injectors at the right pressure and temperature. This gets rid of tough deposits. Most services give you a report showing how much better they work.
Often, cleaning can save injectors from being replaced. It’s cheaper and keeps your engine running smoothly.
DIY Cleaning Procedures
DIY cleaning is good for keeping things clean and fixing small problems. Start with fuel system cleaners in your gas tank, as the maker says.
For tougher cleaning, use pressurized kits that attach to your fuel rail. These kits clean injectors while the engine runs. Always be careful when working with fuel system parts.
- Add fuel system cleaner to a full tank of gas
- Run the engine through several drive cycles
- Use pressurized cleaning kits for stubborn deposits
- Follow all manufacturer safety guidelines
Complete Injector Replacement Guide
Injector replacement is needed when cleaning doesn’t work. Look for signs like misfire codes and bad fuel economy.
Use only top-quality parts for replacement. It’s best to replace all injectors at once for even performance.
Replacing them means lowering fuel pressure, disconnecting wires, and taking out the fuel rail. Make sure new injectors work right before putting them back in.
Step 9: Repairing Vacuum System Leaks
Fixing vacuum leaks in your Toyota engine needs the right tools and careful steps. These leaks let air into your engine, messing with its air-fuel mix. This can cause your engine to idle roughly, not accelerate well, and misfire, damaging it over time.
Vacuum leaks are tough because they hit your engine’s performance hard when it’s idling or moving slowly. At these times, your Toyota vacuum system is working at its highest vacuum levels. Even small leaks can make a big difference in how well your engine runs.
Leak Detection Techniques
Fixing vacuum leaks starts with finding them accurately. Visual checks are key. Look at all vacuum hoses with a flashlight, focusing on where they connect and where they’re exposed to engine heat.
Here are signs of vacuum hose wear:
- Cracks or splits in rubber hoses
- Hard, brittle hose material that lacks flexibility
- Loose connections at fittings and clamps
- Oil contamination that degrades rubber compounds
More advanced methods can pinpoint leaks better. Smoke machines release harmless white smoke into the system, showing leaks as smoke escapes. This method catches small leaks that might be missed by just looking.
The propane enrichment method is another good way to find leaks. Hold an unlit propane torch near suspected leak spots while the engine runs. Engine RPM changes indicate leak presence as the propane enriches the air-fuel mix.
Carburetor cleaner spray is another tool used by pros instead of propane. They watch for RPM changes to find leaks.
| Detection Method | Effectiveness | Equipment Cost | Skill Level Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Good for obvious leaks | Low (flashlight only) | Beginner |
| Smoke Machine | Excellent for all leaks | High ($200-500) | Intermediate |
| Propane Enrichment | Very good | Low ($20-40) | Intermediate |
| Spray Method | Good | Low ($10-15) | Beginner |
Hose and Gasket Replacement
Replacing hoses needs care and the right materials for a lasting fix. Don’t use generic rubber tubing for your car’s vacuum hoses. It can’t handle the heat and vacuum pressure your engine needs.
Get vacuum hose made for cars. It can handle heat, oil, and ozone better than generic stuff. Make sure it’s the right size to fit vacuum fittings well without being too loose or hard to install.
Here’s how to install hoses right:
- Cut hoses with sharp, clean cuts for a good seal
- Clean fitting surfaces before installing
- Apply a little petroleum jelly to help with installation if needed
- Secure connections with the right clamps where needed
Replacing gaskets also needs quality and the right steps. Intake manifold gaskets and other seals must match Toyota’s specs for material and size. Generic gaskets often fail early because of bad materials or wrong sizes.
When putting in intake manifold gaskets, follow your Toyota service manual’s torque sequence. Tightening unevenly can warp the seals and create new leaks. Start with a finger-tight fit, then tighten to the specified torque in the right order.
Clean gasket surfaces well before putting them in. Use the right scrapers and solvents to remove old gasket material completely. Any leftover debris can stop the new gasket from sealing right and cause it to fail early.
Fixing vacuum leaks the right way makes your Toyota’s engine run smoothly and reliably. Use the best detection methods and quality parts for repairs that last. Your engine will thank you with years of good performance.
Preventing Future Toyota Engine Misfire Issues
Smart Toyota owners know that preventing engine misfires saves money and headaches. Preventive maintenance costs far less than major repairs. Your Toyota was built to last, but it needs regular care to perform at its best.
Most misfire problems develop slowly over time. This gives you chances to catch issues early. Small problems become big ones when ignored. Regular attention keeps your engine running smoothly for years.
The key to prevention lies in understanding your vehicle’s needs. Toyota engineers designed maintenance schedules based on real-world testing. Following these guidelines protects your investment and prevents costly breakdowns.
Recommended Maintenance Schedule
Your Toyota maintenance schedule is your roadmap to reliable performance. Toyota’s engineers calculated these intervals through extensive testing. They know exactly when parts wear out and need replacement.
Here are the essential maintenance tasks that prevent misfires:
- Spark plugs: Replace every 30,000 to 100,000 miles depending on your model
- Engine oil: Change every 5,000 to 10,000 miles with Toyota-specified grade
- Air filter: Replace every 15,000 to 30,000 miles or when dirty
- Fuel filter: Change every 30,000 to 60,000 miles
- Fuel system cleaning: Perform every 30,000 miles to prevent deposits
Don’t wait until parts fail completely. Replace spark plugs at recommended intervals even if they seem fine. Worn plugs cause subtle problems that get worse over time.
Clean engine oil protects ignition components from contamination. Dirty oil can affect spark plug performance and cause misfires. Use the exact oil grade Toyota recommends for your engine.
Air and fuel filters keep contaminants out of your engine. Clogged filters restrict airflow and fuel delivery. This creates the perfect conditions for misfires to develop.
Using Quality Replacement Parts
Not all parts are created equal. Quality parts make the difference between reliable performance and frequent problems. Cheap parts often fail quickly and cause additional damage.
Genuine Toyota parts offer the best fit and performance. They’re engineered for your vehicle. Toyota tests these parts extensively to ensure they meet strict quality standards.
When genuine parts aren’t available, choose reputable aftermarket brands. Look for companies that specialize in Toyota applications. These manufacturers understand Toyota’s engineering requirements.
Here’s what to look for in quality replacement parts:
- Warranty coverage: Good parts come with solid warranties
- Brand reputation: Stick with known manufacturers
- Toyota compatibility: Ensure parts meet Toyota specifications
- Professional installation: Have parts installed by qualified technicians
Avoid bargain-basement parts that seem too cheap. These often fail prematurely and can damage other components. The money you save upfront gets spent on additional repairs later.
Quality parts protect your engine and maintain your Toyota’s reliability. They’re designed to work together as a system. Using substandard components breaks this harmony and creates problems.
Address check engine lights immediately. These warnings indicate problems that can lead to misfires. Early intervention prevents minor issues from becoming major repairs.
Your Toyota’s fuel system also needs attention. Use quality gasoline from reputable stations. Add fuel system cleaner periodically to prevent injector deposits. Clean injectors spray fuel properly and prevent misfires.
Preventive maintenance is an investment in your Toyota’s future. Regular care keeps your engine performing like new. It also maintains your vehicle’s resale value and reliability.
Create a maintenance log to track services performed. This helps you stay on schedule and provides valuable records. Future owners will appreciate detailed maintenance history.
Determining When Professional Repair is Necessary
Some engine misfire issues need a skilled automotive technician. While many Toyota owners can do simple repairs, knowing when to ask for help is key. This prevents costly errors and ensures the right diagnosis.
If your misfire issues don’t go away after changing spark plugs and ignition coils, it’s likely a deeper problem. Professional Toyota repair is needed when simple fixes don’t work.
Internal engine damage needs special knowledge and tools. Issues like worn valve guides, damaged pistons, or low compression require major disassembly. These complex engine problems can be very expensive if not done right.
Advanced diagnostic tools are very helpful in finding problems. Shops use oscilloscopes, scan tools, and pressure testers. These tools find issues that simple OBD-II scanners miss.
Thinking about warranties is also important. DIY fixes on complex systems might void your Toyota’s warranty. Professional service keeps your warranty safe and ensures repairs are done right.
It’s also about safety. Working with high-voltage systems and fuel components without the right training and gear is risky. It can lead to injury or even fires.
| Situation | DIY Suitable | Professional Required | Risk Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spark plug replacement | Yes | No | Low |
| Ignition coil replacement | Yes | No | Low |
| Internal engine damage | No | Yes | High |
| Complex fuel system problems | No | Yes | Medium |
| Multiple system failures | No | Yes | High |
If you’ve tried fixing the problem but it keeps coming back, it’s time to get expert help. Automotive technician skills can quickly find the real cause.
Time is also a factor. Professional shops can do complex diagnoses faster than DIY. This saves you time and gets your Toyota running again sooner.
Listen to your gut about repair complexity. If a problem seems too hard, getting professional help avoids frustration and more damage. Quality professional Toyota repair services offer peace of mind and reliable fixes.
Conclusion
Your Toyota needs the best care. With this detailed guide, you can fix most misfire issues. This keeps your vehicle running smoothly.
These steps make fixing your Toyota’s engine easy. Each step helps you find and fix problems. This makes solving misfires straightforward.
Keeping up with maintenance is key. Replacing spark plugs and fixing check engine lights early can save you money. It also prevents big repairs later.
Be patient when you’re figuring out problems. Hurrying can lead to missing issues or wasting money. Make sure to check each part carefully before moving on.
If you’re not sure about repairs, get help from a pro. They have the tools and know-how for tough fixes. Knowing what to look for helps you talk to mechanics better.
Your Toyota will run well if you take care of it. Whether you fix it yourself or get help, knowing how to diagnose problems is important. This keeps your Toyota reliable for many years.
FAQ
What are the most common signs of a Toyota engine misfire?
Signs include rough idling and vibrations, slow acceleration, and jerking while driving. An illuminated check engine light is also common. You might hear popping or backfiring sounds and see black smoke from the exhaust. Strong fuel odors and decreased fuel efficiency are other signs.
Can I drive my Toyota with an engine misfire?
It’s not safe to drive with a misfire. It can damage your engine and make driving dangerous. Unburned fuel reduces acceleration and increases emissions.
What causes engine misfires in Toyota vehicles?
Misfires can be caused by many things. Worn spark plugs and failed ignition coils are common. Clogged fuel injectors and vacuum leaks also cause problems. Dirty mass airflow sensors and low fuel pressure can lead to misfires too.
How much does it cost to fix a Toyota engine misfire?
Costs vary based on the problem. Replacing spark plugs costs 0-300. Ignition coil replacement is 0-600. Fuel injector cleaning or replacement can cost 0-800. More serious issues can cost
FAQ
What are the most common signs of a Toyota engine misfire?
Signs include rough idling and vibrations, slow acceleration, and jerking while driving. An illuminated check engine light is also common. You might hear popping or backfiring sounds and see black smoke from the exhaust. Strong fuel odors and decreased fuel efficiency are other signs.
Can I drive my Toyota with an engine misfire?
It’s not safe to drive with a misfire. It can damage your engine and make driving dangerous. Unburned fuel reduces acceleration and increases emissions.
What causes engine misfires in Toyota vehicles?
Misfires can be caused by many things. Worn spark plugs and failed ignition coils are common. Clogged fuel injectors and vacuum leaks also cause problems. Dirty mass airflow sensors and low fuel pressure can lead to misfires too.
How much does it cost to fix a Toyota engine misfire?
Costs vary based on the problem. Replacing spark plugs costs $100-300. Ignition coil replacement is $200-600. Fuel injector cleaning or replacement can cost $300-800. More serious issues can cost $1,500-5,000 or more.
How often should I replace spark plugs in my Toyota?
Spark plugs should be replaced every 60,000-100,000 miles. Copper plugs last 30,000-50,000 miles. Platinum and iridium plugs can last longer. Check your owner’s manual for the right time for your model.
Can bad fuel cause engine misfires in Toyota vehicles?
Yes, bad fuel can cause misfires. Water, dirt, or old fuel can clog injectors. Using good fuel and adding cleaners can help prevent this.
What OBD-II codes indicate engine misfires in Toyota vehicles?
Common codes include P0300 for random misfires and P0301-P0308 for specific cylinder misfires. These codes help find the problem cylinder.
Should I replace all ignition coils at once or just the failed one?
For high-mileage Toyotas, replace all coils at once. This prevents future failures. For newer vehicles or recent replacements, just replace the failed coil.
How can I prevent engine misfires in my Toyota?
Follow Toyota’s maintenance schedule. This includes regular spark plug and oil changes. Replace air and fuel filters and clean the fuel system. Use quality parts and address check engine lights quickly.
Can a vacuum leak cause engine misfires?
Yes, vacuum leaks can cause misfires. They let unmetered air into the engine. This disrupts the air-fuel mixture. Common leak sources include vacuum hoses and intake manifold gaskets.
When should I seek professional help for Toyota engine misfires?
Get professional help if simple repairs don’t work. If multiple systems are involved or if you suspect internal damage. Also, seek help if your Toyota is under warranty or if safety concerns arise.
Can engine misfires damage my Toyota’s catalytic converter?
Yes, misfires can damage the catalytic converter. Unburned fuel can overheat it. This can melt or clog the converter. Prompt repair is key to avoid this expensive damage.
,500-5,000 or more.
How often should I replace spark plugs in my Toyota?
Spark plugs should be replaced every 60,000-100,000 miles. Copper plugs last 30,000-50,000 miles. Platinum and iridium plugs can last longer. Check your owner’s manual for the right time for your model.
Can bad fuel cause engine misfires in Toyota vehicles?
Yes, bad fuel can cause misfires. Water, dirt, or old fuel can clog injectors. Using good fuel and adding cleaners can help prevent this.
What OBD-II codes indicate engine misfires in Toyota vehicles?
Common codes include P0300 for random misfires and P0301-P0308 for specific cylinder misfires. These codes help find the problem cylinder.
Should I replace all ignition coils at once or just the failed one?
For high-mileage Toyotas, replace all coils at once. This prevents future failures. For newer vehicles or recent replacements, just replace the failed coil.
How can I prevent engine misfires in my Toyota?
Follow Toyota’s maintenance schedule. This includes regular spark plug and oil changes. Replace air and fuel filters and clean the fuel system. Use quality parts and address check engine lights quickly.
Can a vacuum leak cause engine misfires?
Yes, vacuum leaks can cause misfires. They let unmetered air into the engine. This disrupts the air-fuel mixture. Common leak sources include vacuum hoses and intake manifold gaskets.
When should I seek professional help for Toyota engine misfires?
Get professional help if simple repairs don’t work. If multiple systems are involved or if you suspect internal damage. Also, seek help if your Toyota is under warranty or if safety concerns arise.
Can engine misfires damage my Toyota’s catalytic converter?
Yes, misfires can damage the catalytic converter. Unburned fuel can overheat it. This can melt or clog the converter. Prompt repair is key to avoid this expensive damage.