Common Toyota Catalytic Converter Problems Explained
Your vehicle’s emissions system is very important. It helps reduce harmful pollutants in the air. If it starts to fail, you’ll see warning signs that you can’t ignore.
Many drivers notice their car uses more fuel and doesn’t run as well when the exhaust system gets old. These problems can start small but get worse fast if not fixed.
This guide covers the most common catalytic converter failure signs. We’ll show you when your car needs help and what to do next.
We’ll talk about spotting early signs, understanding repair costs, and how to prevent problems. Whether it’s a check engine light or odd noises from your exhaust, we’ve got you covered.
Key Takeaways
- Spotting issues early can save you from expensive repairs and engine damage.
- Common signs include using more fuel, poor acceleration, and strange exhaust sounds.
- Regular maintenance and using good fuel can make your exhaust parts last longer.
- Getting a professional to check your car is key to finding out what’s wrong.
- Replacing parts can cost a lot, depending on your car and what needs fixing.
- Ignoring warning signs can lead to a complete breakdown and very high repair costs.
Understanding Your Toyota’s Catalytic Converter System
Your Toyota’s catalytic converter is key in reducing pollution. It changes harmful exhaust gases into safer emissions. This technology is in your vehicle’s exhaust system, working all the time to protect our planet. Knowing how it works helps you spot issues early and keep your Toyota in top shape.
What Is a Catalytic Converter and How It Works
The catalytic converter function focuses on chemical reactions that clean pollutants. Inside, a honeycomb structure coated with metals like platinum, palladium, and rhodium makes these reactions happen. They turn harmful gases into water vapor and carbon dioxide.
This process needs high temperatures, between 400 to 800 degrees Fahrenheit. That’s why your Toyota might emit more during cold starts.
Toyota’s Catalytic Converter Design Features
Toyota’s emissions control uses advanced engineering for each engine. Their converters have multiple chambers and special coatings for better efficiency and longer life. Toyota also uses oxygen sensors before and after the converter to check its performance.
Newer Toyota models often have more than one converter. This setup ensures better pollution reduction and meets strict environmental rules.
Location in Different Toyota Models
The location of exhaust system components changes in Toyota models. In cars like the Camry and Corolla, the main converter is near the engine for quick heating.
In SUVs and trucks like the Highlander and Tacoma, there are more converters. The main one is near the engine, and the others are further down. This setup works well for big engines and makes maintenance easier.
Toyota Catalytic Converter Problems You Need to Know
Four main issues can harm Toyota catalytic converters and affect emissions. These problems can start slowly or happen suddenly. Spotting them early can save you from costly fixes. Knowing about these failures helps keep your car running well.
Clogging and Contamination Issues
A clogged catalytic converter is a big problem for Toyota owners. Carbon builds up inside, blocking exhaust flow. Oil leaks from engine seals add to the blockage.
Converter contamination happens when coolant gets into the exhaust system. This can damage the converter’s precious metal. It makes the converter less effective, leading to poor fuel efficiency and check engine lights.
Physical Damage from Road Debris
Driving on rough roads can harm your Toyota’s exhaust system. Big rocks, construction debris, and potholes can damage the converter. Speed bumps can also cause catalytic converter damage in low vehicles.
Driving off-road increases the risk of damage. Scraping against rocks or stumps can puncture the converter. Even small dents can mess up airflow and efficiency.
Overheating Problems
Engine misfires send unburned fuel to the converter, causing it to overheat. Temperatures can reach over 2,000 degrees Fahrenheit. This can melt the converter’s internal parts.
Ignition system failures also raise the risk of overheating. Worn spark plugs and faulty sensors can send more unburned fuel to the converter. Regular maintenance helps avoid these overheating issues.
Theft-Related Damage
Catalytic converter theft is a big problem in the US. Toyota Prius models are at high risk. Thieves can remove converters quickly with simple tools.
Theft often damages other exhaust parts, raising repair costs. Park in well-lit areas and use anti-theft devices to protect your car. Some insurance covers catalytic converter damage from theft, but you might have to pay a deductible.
How to Identify Catalytic Converter Failure Signs
Spotting catalytic converter issues early saves money and prevents engine damage. Your Toyota will show specific signs when it starts to fail. Knowing these catalytic converter symptoms helps you fix problems fast.
Early detection protects your engine from expensive damage. Most Toyota owners can spot these warning signs easily.
Recognizing Engine Performance Symptoms
Changes in engine performance are often the first signs of converter problems. You might notice sluggish acceleration when merging onto highways or climbing hills. Your Toyota may struggle to keep speed during normal driving.
Reduced engine performance shows in several ways. The vehicle feels like it’s working harder to achieve the same power. You might find it hard to start the engine or notice it runs roughly at idle.
Poor fuel economy is another clear sign. If you’re filling up more often despite normal driving, your converter might be forcing the engine to work inefficiently.
Spotting Exhaust System Warning Signs
Unusual sounds from your exhaust system indicate converter problems. Rattling noises during startup or while driving suggest loose internal components inside the converter.
A strong sulfur smell from your exhaust is a serious warning sign. This rotten egg odor means the converter isn’t properly processing emissions. The smell becomes more noticeable during acceleration or when the engine is under load.
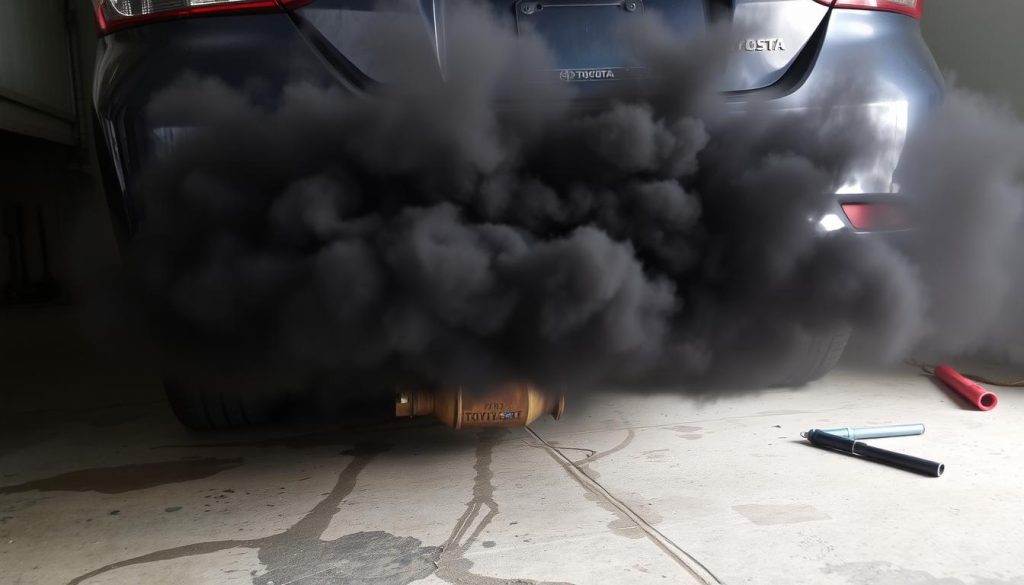
Dark or unusual exhaust smoke also signals converter issues. Normal exhaust should be nearly invisible on most days.
Understanding Dashboard Warning Lights
The check engine light often lights up when converter efficiency drops. This warning light shouldn’t be ignored, as it often indicates serious emissions problems.
Specific trouble codes help identify converter issues. The P0420 code directly relates to catalytic converter performance and requires immediate attention. P0430 codes also indicate converter problems in vehicles with dual exhaust systems.
| Symptom Category | Warning Signs | Urgency Level | Potential Damage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Engine Performance | Sluggish acceleration, poor fuel economy | Medium | Engine strain, increased wear |
| Exhaust System | Rattling sounds, sulfur smell | High | Complete converter failure |
| Dashboard Alerts | Check engine light, P0420 codes | High | Failed emissions testing |
| Physical Signs | Dark exhaust smoke, visible damage | Critical | Environmental violations |
Failed emissions tests during state inspections clearly indicate converter problems. Most states require passing emissions tests for vehicle registration renewal.
Step-by-Step Guide to Diagnosing Converter Problems
To find out if your Toyota’s catalytic converter needs fixing, follow a detailed process. This includes looking closely and using special tools. This way, you can tell if it needs cleaning, fixing, or replacing. It saves you money by finding the exact problem before spending too much.
Performing Visual Inspection
Begin by doing a catalytic converter diagnosis with a visual check. Use jack stands to lift your car and look for damage. Look for dents, cracks, or missing parts that show physical damage.
Also, check the converter’s outer shell and where it’s mounted. Look for loose heat shields that make noise when you accelerate. Check the pipes for rust, holes, or damage that affects exhaust flow.
Also, watch for signs of theft, like cut marks or damaged clamps around the converter. These signs show someone has tried to tamper with it.
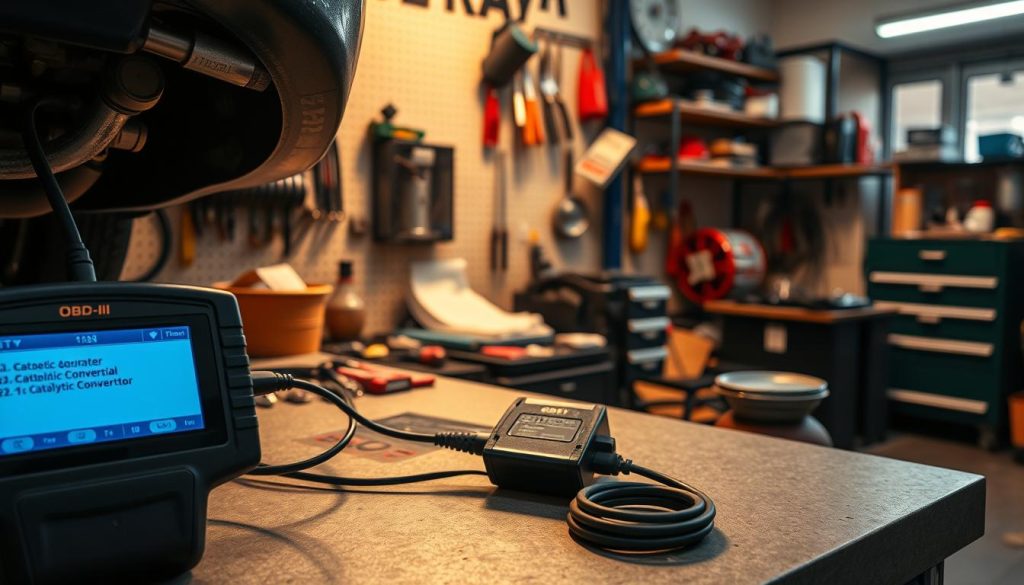
Using OBD-II Scanner for Error Codes
An OBD-II scanner is key for getting important info from your Toyota’s computer. Plug it into the diagnostic port, usually under the dashboard near the driver’s left knee.
The most common code is the P0420 code, which means your converter isn’t working right. It shows your converter isn’t handling emissions well and might need fixing.
Other codes you might see include:
- P0430 – Second converter bank issues in V6 engines
- P0171/P0174 – Lean fuel conditions damaging converters
- P0136/P0141 – Oxygen sensor problems affecting converter performance
After noting the codes, clear them and drive your Toyota for a few miles. If the codes come back right away, you need to fix the problem fast.
When to Use Professional Testing Methods
When simple checks don’t give you answers, it’s time for a pro. Mechanics use special tools that go beyond what an OBD-II scanner can do.
They use exhaust gas analysis to check emissions levels. They also do back-pressure tests to find blockages that hurt engine performance.
They use infrared guns to check if the converter is working right by measuring heat. They also check oxygen sensors and fuel system parts that affect the converter.
Get a pro if you see many error codes at once or if problems keep coming back after simple fixes.
Toyota Models Most Vulnerable to Converter Issues
Some Toyota vehicles are more likely to have catalytic converter problems. This is due to their design, how they are used, and being targeted by thieves. Knowing which models are at risk helps you get ready and take steps to prevent problems.
Each Toyota model has its own challenges for the converter. Some have design issues, while others are targeted because they are popular or easy to get to.
Hybrid System Challenges
The Toyota Prius catalytic converter has special problems because of its hybrid design. The converter works at lower temperatures because the electric motor helps the gasoline engine a lot.
This cooler temperature makes it harder for the converter to burn off all contaminants. This leads to faster clogging and less efficiency over time.
Thieves also target Prius models a lot because their converters have more precious metals. The easy access under the car makes these vehicles tempting targets in parking lots and driveways.
Sedan Reliability Concerns
Toyota Camry converter problems often start around 100,000 miles, mainly in 2007-2017 models. These popular sedans often get a P0420 diagnostic code because of oxygen sensor failures.
High-mileage Camrys have converter substrate breakdown from normal wear and heat. The converter’s internal honeycomb structure wears out with age and heat.
Regular maintenance is key to avoid early converter failure in these vehicles. Ignoring engine problems can quickly harm the converter’s delicate parts.
Truck-Specific Risk Factors
Toyota Tacoma and Tundra trucks have their own challenges for their Toyota Tacoma emissions systems. Their high ground clearance makes converters easy for thieves to access with basic tools.
Off-road driving can damage these trucks, including the converter, from rocks and debris. The converter’s location under the truck makes it prone to damage during trail driving.
These trucks’ bigger engines can cause converter overheating if maintenance is skipped. Keeping the cooling system in check is vital to avoid heat damage to the converter.
How to Protect Your Toyota from Catalytic Converter Theft
To protect your Toyota from catalytic converter theft, use a mix of physical barriers, smart choices, and insurance. Toyota vehicles are often targeted because their converters have valuable metals. They are also easy to get to. Taking action now can save you a lot of money and trouble later.
Catalytic converter theft prevention means knowing thieves work fast and quietly. They can take an unprotected converter in under five minutes. So, prevention is better than trying to catch them.
Physical Barriers and Security Systems
Using anti-theft devices is the best way to stop converter theft. Metal shields attach to your car’s underside, covering the converter. This makes thieves work harder and noisier.
Cable and clamp systems are also effective. They use strong cables and clamps to keep the converter in place. Most thieves will look for easier targets when they see these systems.
Motion-activated alarms and vibration sensors add more protection. They sound loud alarms when someone tries to get to your car’s underside. This scares thieves away.
Strategic Parking Decisions
Where you park affects your risk of theft. Parking in well-lit, busy areas deters thieves. Near building entrances, security cameras, or walkways is best.
Garage parking is the safest option. If you can’t park in a garage, choose spots near other cars or walls. Avoid empty lots or dark streets at night.
Insurance Protection Options
Auto insurance usually covers converter theft, but policies differ. Check your deductible and coverage limits. Some insurers now offer specific coverage for converter theft.
Keep records of your converter’s serial numbers and take photos for insurance. If your Toyota’s value is close to the replacement cost, consider gap coverage. Converter replacement can cost over $3,000 for popular models like the Prius.
“The best defense against catalytic converter theft is making your vehicle a harder target than the one parked next to it.”
Essential Maintenance Steps to Prevent Converter Failure
Preventive maintenance is key to avoiding costly catalytic converter problems in your Toyota. Taking care of your converter early saves a lot of money. Smart maintenance practices can save you thousands of dollars and keep your car running well for years.
Your converter works closely with other engine systems. Keeping these systems healthy protects your converter. Regular maintenance of key areas is vital for its longevity.
Staying on Track with Your Maintenance Schedule
Your engine maintenance schedule is critical for converter protection. Regular oil changes prevent contaminated oil from reaching your converter. Clean oil means clean combustion, which reduces converter stress.
Replace air filters as Toyota recommends. Dirty filters lead to rich fuel mixtures that overwork your converter. Spark plugs also need attention – worn plugs cause misfires that dump raw fuel into the converter.
Don’t overlook cooling system maintenance. Overheating damages converter materials quickly. Regularly check coolant levels and flush the system as needed.
Making Smart Fuel and Additive Choices
Fuel quality greatly affects your converter’s health and lifespan. Top-tier gasoline contains detergents that keep fuel systems clean. These additives promote complete combustion, reducing harmful deposits in your converter.
Avoid discount gas stations that may sell lower-quality fuel. Higher sulfur content and fewer cleaning agents can harm your converter over time. Spending a few extra cents per gallon saves hundreds later.
Use fuel system cleaners occasionally, but choose products designed for cars with converters. Some additives actually damage converter materials. Stick with Toyota-approved products for best results.
Developing Converter-Friendly Driving Patterns
Your driving habits significantly affect converter life. Allow your engine to warm up before aggressive driving. Converters need operating temperature to work effectively.
Limit short trips when possible. Frequent cold starts prevent converters from reaching optimal temperature. Highway driving helps burn off deposits and maintains proper converter function.
Address performance issues immediately. Rough idling, hesitation, or check engine lights often signal problems that can damage your converter. Quick action prevents small issues from becoming expensive repairs.
How to Clean a Clogged Toyota Catalytic Converter
A clogged catalytic converter doesn’t always mean you need to replace it. Using the right catalytic converter cleaning methods can save you a lot of money. The success of cleaning depends on how bad the clog is and what’s causing it.
First, check how bad your converter is. If it’s just a little dirty, cleaning might work. But if it’s really damaged, you’ll need a pro to look at it.
Safe DIY Cleaning Methods
DIY converter cleaning starts with special cleaners for your fuel system. Follow the instructions to add the cleaner to your gas. Then, drive fast for a long time to get the converter hot.
The “Italian tune-up” method is another way. It involves driving fast to burn off carbon. But, this only works for light dirt and not if the converter is damaged.
Professional Cleaning Options
For really dirty converters, professionals have better solutions. They might take it out for a deep clean or use special cleaning solutions on your car. This way, they get all the dirt out.
Getting a pro to clean your catalytic converter costs about $200-500. It’s worth it if it makes your converter last longer and work better.
Determining When Replacement Is Necessary
If cleaning doesn’t fix your converter, you might need a new one. Damage that can’t be cleaned out means it’s time for a replacement. This is true for things like cracks or melted parts.
How old your converter is also matters. Ones over 150,000 miles might not clean well and could fail again soon.
“Sometimes the most expensive repair is the one you keep putting off.”
Complete Guide to Catalytic Converter Replacement
When your Toyota’s catalytic converter fails, it’s key to know your options. Catalytic converter replacement is a big deal. It affects your car’s performance and your budget for a long time.
Weighing Your Parts Options
The OEM vs aftermarket debate is about quality vs cost. Toyota’s OEM converters are guaranteed to fit right and last 10-15 years. They’re made for your car’s engine and emissions.
OEM converters cost $800-2,500, depending on your Toyota. Aftermarket converters are cheaper, $200-800. But, their quality can vary a lot.
Good aftermarket converters can be as good as OEM ones. Make sure they meet EPA and CARB standards for your car to avoid problems later.
Tackling the DIY Approach
Doing it yourself can save money if you know how. You’ll need to raise the car, remove oxygen sensors, and install the new converter. It’s a job for those with mechanical skills and the right tools.
It’s not easy, with rusted bolts and tight spaces. If done wrong, it can cause leaks, poor performance, or early failure.
Professional Installation Advantages
For most Toyota owners, getting a pro to do it is worth the extra cost. They have the skills and tools to handle tough jobs. They can also find and fix other problems that might affect the converter.
Professional installation usually comes with warranties. This gives you peace of mind. Many shops offer payment plans to help with the cost, ensuring it’s done right.
Choosing a pro means your car is fixed right, and you get warranties. DIY can’t offer the same level of service and protection.
Cost Breakdown for Toyota Converter Repairs
Knowing the cost of catalytic converter repairs helps Toyota owners make better choices for their cars. Catalytic converter cost can be a few hundred dollars or several thousand. The price depends on your Toyota model and the repair needed.
Parts Pricing by Toyota Model
Prices for converters differ across Toyota models. The cheapest options are usually found in compact cars:
- Toyota Corolla: $300-800 aftermarket, $600-1,200 OEM
- Toyota Camry: $400-1,000 aftermarket, $800-1,800 OEM
- Toyota Tacoma/Tundra: $600-1,500 aftermarket, $1,200-2,500 OEM
- Toyota Prius: $800-2,000 aftermarket, $1,500-3,000 OEM
Hybrid cars like the Prius cost more because of their special design. They have more precious metals, which increases the cost.
Labor Costs and Time Estimates
Toyota repair costs include parts and labor. Labor costs usually range from $80-150 per hour.
Replacing converters that are easy to get to takes 1-3 hours. More complex jobs that need more converters or are harder to reach take 4-6 hours. If oxygen sensors also need to be replaced, it can take even longer.
Money-Saving Strategies
There are ways to save money on repairs:
- Shop around for quotes from different shops
- Consider independent mechanics for lower labor rates
- Time repairs during off-peak seasons for better prices
- Ask about cash discounts or package deals
Avoid very cheap options that might use low-quality parts. Cheap converters can fail early, leading to more costs later.
Navigating Legal Requirements and Emissions Testing
Emissions compliance is more than just a working catalytic converter in your Toyota. Understanding your local legal obligations helps you avoid costly penalties and registration problems. Different states have varying requirements that directly impact your vehicle maintenance decisions.
Understanding State Emissions Standards
State emissions standards vary across the United States. California, New York, and Texas have the strictest rules. Other states focus more on safety inspections. Most states require emissions testing every one to two years for vehicle registration renewal.
Your location determines which catalytic converter types are acceptable. CARB-compliant converters are mandatory in California and states following California’s standards. EPA-approved units work fine in most other locations.
Preparing for Inspection Requirements
Successful emissions testing requires more than just a working converter. Your Toyota’s onboard diagnostic system must show no active error codes. All emissions-related components need to operate within specified parameters.
Address any check engine lights before your inspection date. Some states require specific drive cycles after repairs. This process can take several days of normal driving.
Legal Consequences of Non-Compliance
Failed emissions compliance prevents vehicle registration renewal, making road use illegal. Many states impose fines for non-compliance, while others require immediate repairs before re-testing.
Federal law prohibits tampering with or removing catalytic converters. Violations result in substantial penalties. Insurance companies may deny claims for vehicles not meeting emissions standards, creating additional financial risks for owners.
How to Choose Professional Help for Converter Issues
Choosing the right help for your Toyota’s catalytic converter problems is key. At professional service centers, skilled technicians can find and fix the issue. Knowing when to seek help and choosing the right provider saves time, money, and frustration.
Emergency Warning Signs
Some symptoms need quick action from a professional mechanic. If your Toyota loses power, smokes a lot, or has a loud exhaust, get help fast.
Strong sulfur smells, engine overheating, or losing acceleration are dangers. Don’t ignore flashing check engine lights – they often mean misfires that can harm your converter.
Choosing the Right Service Provider
Choosing a good repair shop means checking their credentials and reviews. Look for ASE-certified technicians with Toyota experience.
Independent shops often cost less than dealerships but keep high standards. Ask about warranties on parts and labor, as good shops back their work.
Key Questions for Your Mechanic
Good automotive diagnostics start with the right questions. Ask about error codes and their meanings. Also, ask about repair options and why they suggest certain ones.
Get a written estimate of all costs. Don’t hesitate to request a second opinion for big repairs, like replacing the catalytic converter. It’s a big investment that needs careful thought.
Taking Control of Your Toyota’s Catalytic Converter Health
Your Toyota’s catalytic converter is key to a smooth ride and protecting our planet. Knowing the signs of trouble and acting early can save you from big repair bills.
Looking after your catalytic converter is easy. Just use good fuel, stick to your maintenance schedule, and fix engine issues fast. These steps can make your converter last longer and save you money.
Spotting problems early is super important. If your dashboard lights up, you see weird smoke, or your car uses more gas, act fast. An OBD-II scanner can show you exactly what’s wrong.
Keeping your car safe from thieves is also important. Choose safe parking spots and use anti-theft devices. This is cheaper than fixing or replacing your converter.
Your catalytic converter is not just about performance. It also keeps you legal on the road. If it fails, you might not pass emissions tests, leading to fines and trouble.
Fixing your converter issues quickly is a smart move. You can do it yourself or get a pro to help. Either way, your Toyota will run better and be kinder to the environment for years.
FAQ
What are the most common signs that my Toyota’s catalytic converter is failing?
Signs include slow acceleration and less engine power. You might hear unusual noises from the exhaust. A strong sulfur smell and an illuminated check engine light are also signs.
Bad fuel economy and failing emissions tests are other indicators. Your Toyota might feel like it’s working harder than usual.
Why are Toyota Prius catalytic converters frequently targeted by thieves?
Prius converters are stolen because they have valuable metals like platinum and rhodium. They’re easy to get to and can be removed quickly. The lower temperatures also mean the metals last longer, making them more valuable.
How much does it typically cost to replace a catalytic converter on different Toyota models?
Prices vary by model. Corolla converters cost 0-800 (aftermarket) or 0-1,200 (OEM). Camry converters are 0-1,000 (aftermarket) or 0-1,800 (OEM).
Tacoma/Tundra converters range from 0-1,500 (aftermarket) or
FAQ
What are the most common signs that my Toyota’s catalytic converter is failing?
Signs include slow acceleration and less engine power. You might hear unusual noises from the exhaust. A strong sulfur smell and an illuminated check engine light are also signs.
Bad fuel economy and failing emissions tests are other indicators. Your Toyota might feel like it’s working harder than usual.
Why are Toyota Prius catalytic converters frequently targeted by thieves?
Prius converters are stolen because they have valuable metals like platinum and rhodium. They’re easy to get to and can be removed quickly. The lower temperatures also mean the metals last longer, making them more valuable.
How much does it typically cost to replace a catalytic converter on different Toyota models?
Prices vary by model. Corolla converters cost $300-800 (aftermarket) or $600-1,200 (OEM). Camry converters are $400-1,000 (aftermarket) or $800-1,800 (OEM).
Tacoma/Tundra converters range from $600-1,500 (aftermarket) or $1,200-2,500 (OEM). Prius converters are the most expensive at $800-2,000 (aftermarket) or $1,500-3,000 (OEM). Labor costs add $80-150 per hour.
Can I clean my Toyota’s catalytic converter instead of replacing it?
Cleaning can work for lightly contaminated converters. Use fuel system cleaners or drive on highways to burn off deposits. Professional cleaning costs $200-500.
But, cleaning won’t fix physical damage or severely clogged units. These need to be replaced.
What’s the difference between OEM and aftermarket catalytic converters for Toyota vehicles?
OEM converters fit perfectly, perform well, and last 10-15 years. They cost $800-2,500. Aftermarket converters cost $200-800 and can be nearly as good if you choose quality brands.
But, cheap alternatives might fail early. Make sure aftermarket units meet EPA and CARB standards for your Toyota.
How can I protect my Toyota from catalytic converter theft?
Use anti-theft devices like shields or alarms. Park in well-lit areas or garages. Etch your VIN number on the converter for traceability.
Have insurance that covers theft. Document serial numbers and photos for insurance purposes.
What maintenance steps can prevent catalytic converter problems in my Toyota?
Keep up with regular maintenance like oil changes and air filter replacements. Use quality fuel and avoid cheap gas. Address check engine lights quickly.
Let your engine warm up properly. Take regular highway drives to keep the converter at the right temperature.
Which Toyota models are most prone to catalytic converter issues?
Prius converters face unique challenges due to lower temperatures and theft. Camry models (2007-2017) often get P0420 codes around 100,000 miles.
Tacoma and Tundra trucks are at risk of theft and physical damage from off-road driving or overheating.
What does the P0420 error code mean for my Toyota?
P0420 means your converter isn’t processing emissions well. This code needs immediate attention to avoid failed emissions tests and engine damage. Related codes include P0430 for V6 engines and P0171/P0174 for lean fuel conditions.
When should I seek professional help for catalytic converter issues?
Get professional help if your Toyota loses power, produces smoke, or has loud noises. Strong sulfur smells, overheating, or a flashing check engine light also require immediate attention.
Do I need a CARB-compliant catalytic converter for my Toyota?
Yes, if you live in California or states with California’s emissions standards. EPA-approved units are okay in most other states. Check your local emissions requirements before buying a replacement converter.
How long do Toyota catalytic converters typically last?
OEM converters last 10-15 years or 100,000-150,000 miles with proper care. Driving habits, fuel quality, and maintenance affect lifespan. High-quality aftermarket converters last 8-12 years, while cheap ones might fail in 2-5 years.
,200-2,500 (OEM). Prius converters are the most expensive at 0-2,000 (aftermarket) or
FAQ
What are the most common signs that my Toyota’s catalytic converter is failing?
Signs include slow acceleration and less engine power. You might hear unusual noises from the exhaust. A strong sulfur smell and an illuminated check engine light are also signs.
Bad fuel economy and failing emissions tests are other indicators. Your Toyota might feel like it’s working harder than usual.
Why are Toyota Prius catalytic converters frequently targeted by thieves?
Prius converters are stolen because they have valuable metals like platinum and rhodium. They’re easy to get to and can be removed quickly. The lower temperatures also mean the metals last longer, making them more valuable.
How much does it typically cost to replace a catalytic converter on different Toyota models?
Prices vary by model. Corolla converters cost $300-800 (aftermarket) or $600-1,200 (OEM). Camry converters are $400-1,000 (aftermarket) or $800-1,800 (OEM).
Tacoma/Tundra converters range from $600-1,500 (aftermarket) or $1,200-2,500 (OEM). Prius converters are the most expensive at $800-2,000 (aftermarket) or $1,500-3,000 (OEM). Labor costs add $80-150 per hour.
Can I clean my Toyota’s catalytic converter instead of replacing it?
Cleaning can work for lightly contaminated converters. Use fuel system cleaners or drive on highways to burn off deposits. Professional cleaning costs $200-500.
But, cleaning won’t fix physical damage or severely clogged units. These need to be replaced.
What’s the difference between OEM and aftermarket catalytic converters for Toyota vehicles?
OEM converters fit perfectly, perform well, and last 10-15 years. They cost $800-2,500. Aftermarket converters cost $200-800 and can be nearly as good if you choose quality brands.
But, cheap alternatives might fail early. Make sure aftermarket units meet EPA and CARB standards for your Toyota.
How can I protect my Toyota from catalytic converter theft?
Use anti-theft devices like shields or alarms. Park in well-lit areas or garages. Etch your VIN number on the converter for traceability.
Have insurance that covers theft. Document serial numbers and photos for insurance purposes.
What maintenance steps can prevent catalytic converter problems in my Toyota?
Keep up with regular maintenance like oil changes and air filter replacements. Use quality fuel and avoid cheap gas. Address check engine lights quickly.
Let your engine warm up properly. Take regular highway drives to keep the converter at the right temperature.
Which Toyota models are most prone to catalytic converter issues?
Prius converters face unique challenges due to lower temperatures and theft. Camry models (2007-2017) often get P0420 codes around 100,000 miles.
Tacoma and Tundra trucks are at risk of theft and physical damage from off-road driving or overheating.
What does the P0420 error code mean for my Toyota?
P0420 means your converter isn’t processing emissions well. This code needs immediate attention to avoid failed emissions tests and engine damage. Related codes include P0430 for V6 engines and P0171/P0174 for lean fuel conditions.
When should I seek professional help for catalytic converter issues?
Get professional help if your Toyota loses power, produces smoke, or has loud noises. Strong sulfur smells, overheating, or a flashing check engine light also require immediate attention.
Do I need a CARB-compliant catalytic converter for my Toyota?
Yes, if you live in California or states with California’s emissions standards. EPA-approved units are okay in most other states. Check your local emissions requirements before buying a replacement converter.
How long do Toyota catalytic converters typically last?
OEM converters last 10-15 years or 100,000-150,000 miles with proper care. Driving habits, fuel quality, and maintenance affect lifespan. High-quality aftermarket converters last 8-12 years, while cheap ones might fail in 2-5 years.
,500-3,000 (OEM). Labor costs add -150 per hour.
Can I clean my Toyota’s catalytic converter instead of replacing it?
Cleaning can work for lightly contaminated converters. Use fuel system cleaners or drive on highways to burn off deposits. Professional cleaning costs 0-500.
But, cleaning won’t fix physical damage or severely clogged units. These need to be replaced.
What’s the difference between OEM and aftermarket catalytic converters for Toyota vehicles?
OEM converters fit perfectly, perform well, and last 10-15 years. They cost 0-2,500. Aftermarket converters cost 0-800 and can be nearly as good if you choose quality brands.
But, cheap alternatives might fail early. Make sure aftermarket units meet EPA and CARB standards for your Toyota.
How can I protect my Toyota from catalytic converter theft?
Use anti-theft devices like shields or alarms. Park in well-lit areas or garages. Etch your VIN number on the converter for traceability.
Have insurance that covers theft. Document serial numbers and photos for insurance purposes.
What maintenance steps can prevent catalytic converter problems in my Toyota?
Keep up with regular maintenance like oil changes and air filter replacements. Use quality fuel and avoid cheap gas. Address check engine lights quickly.
Let your engine warm up properly. Take regular highway drives to keep the converter at the right temperature.
Which Toyota models are most prone to catalytic converter issues?
Prius converters face unique challenges due to lower temperatures and theft. Camry models (2007-2017) often get P0420 codes around 100,000 miles.
Tacoma and Tundra trucks are at risk of theft and physical damage from off-road driving or overheating.
What does the P0420 error code mean for my Toyota?
P0420 means your converter isn’t processing emissions well. This code needs immediate attention to avoid failed emissions tests and engine damage. Related codes include P0430 for V6 engines and P0171/P0174 for lean fuel conditions.
When should I seek professional help for catalytic converter issues?
Get professional help if your Toyota loses power, produces smoke, or has loud noises. Strong sulfur smells, overheating, or a flashing check engine light also require immediate attention.
Do I need a CARB-compliant catalytic converter for my Toyota?
Yes, if you live in California or states with California’s emissions standards. EPA-approved units are okay in most other states. Check your local emissions requirements before buying a replacement converter.
How long do Toyota catalytic converters typically last?
OEM converters last 10-15 years or 100,000-150,000 miles with proper care. Driving habits, fuel quality, and maintenance affect lifespan. High-quality aftermarket converters last 8-12 years, while cheap ones might fail in 2-5 years.